我想讨论的问题其实并不局限于MBTI人格分类体系中的INFJ型人,那就是,当你满怀热情的对待别人,却得不到相同的回报,久而久之往往心灰意冷,这时该怎样自处和与他人相处?概括起来,就像俗话说的,常常”用热脸贴了冷屁股”,话糙理不糙。
回想起来,对我而言,这个问题并不是现在才出现的。随着我的成长,我渐渐对人和人之间的共性和差别有了更多认识,特别是在文超的推荐下读了一些和人格分类有关的书籍文章,我知道了一个基本的常识:人和人之间天然地具有不同的性格,这就决定了他们截然不同的行为方式。明白了这一点和不同性格人的行为特点,我回忆过去的经历时就有了依据,许多问题似乎变得明晰了——为什么在某种情况下,自己和其他人会有那么不同的感受?在不同的感受下,自然有了不同的行动。
所以,当我在许多情况下困惑和纠结于自己和别人的行为不同,并常常觉得浪费感情甚至受到伤害时,其实根源还是人的性格问题。开头说的”热情却得不到回报”就是这类困惑的典型代表。至于为什么我的感受更为强烈,我想,这是因为作为理想主义者的INFJ型人,他们对人际关系的关注、对他人感情的细微认知和对世界的强烈理想主义色彩使得他们过于敏感。当”理想”破灭时,就有了被伤害的感觉。
可是,明白了这一点,只是让我再次遇到问题时的换位思考有了理论依据(尽管INFJ的移情能力本身就不弱),心中的怨念却总也放不下。当再有人说起,你是好人啊云云,我竟变得不耐烦,心里只想着好人又有什么用,大概这是热情被浇灭后的暂时性冷漠吧。
INFJ的理想世界是,我为人人,人人为我,彼此关爱,和谐发展。这和施恩图报还是有区别的,但是这种理想和施恩图报都希望别人对自己也总有积极的反馈,这是常常失望的根源。我曾摘录了《沉思录》上的一段话,
"有一种人,在加惠与人的时候,希望对方要有回报。另一种人,虽不作此想,但在内心总念念不忘对方是他的债务人,总觉得自己做了一件好事。但还另有一种人则行若无事,有如一颗葡萄树,一旦生出了一束葡萄,并不希望什么报酬。"
我希望以此自勉,发现自己的境界还差得太远,根本做不到行若无事,只好慢慢修身。
好吧,我承认,我只是提出了困惑,却根本没有解脱。
Update 2012-4-12:
本文讨论的话题,可以参考阅读:
“好人”综合症
虽然不完全切题,里面提到的心理分析还是让我有所反省。
Published:
15 Apr 2011
今年开始我需要同时使用实验室的电脑和寝室的笔记本,对文件同步的需求变得迫切起来。试验了几个云存储的产品后,我还是选择了微软的windows live mesh。它的功能非常简单,在一台电脑上选择需要同步的文件夹,以后在其他机器上,如果需要该文件夹的内容,只需要安装mesh,选择同步就可以了。
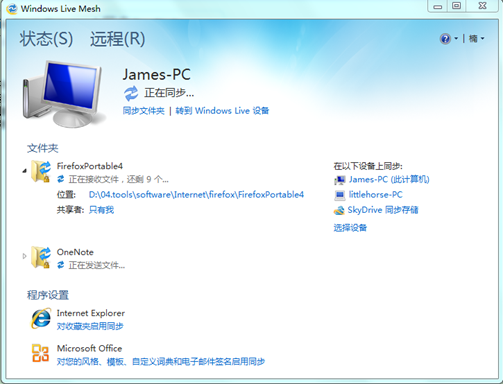
上面是Mesh的界面截图。我现在只需要同步Firefox和OneNote两个文件夹,图中,James-PC和littlehorse-PC是分别在实验室和寝室的电脑,SkyDrive是云端的存储空间,也就是负责接收文件的中间点。微软免费提供了5G的大小,对于一般文件的备份是非常充足的。
使用了文件夹同步后,不论在哪台电脑上做了OneNote笔记,到另外一处都可以看到相同的结果;如果本地数据不幸丢失,也可以第一时间恢复。
国内的几个存储产品,我不太习惯的是需要设置专门的文件夹给同步软件使用,使用起来远不如Mesh简洁。如果你只想简单的同步几个文件夹的话,我推荐Live Mesh。
Published:
13 Apr 2011
因为对这个行业的喜爱,一直也喜欢看有关IT的各种评论文章,google reader里订阅最多的也就是这一类博客,有一段时间还买过几期《IT时代周刊》。看得多了,渐渐发现这类文章中,有真知灼见的少之又少,以至于再看到"某公司为什么不做某某业务?这显然是最有前途的"等等此类言论也就匆匆跳过了。旁观者清也许有时成立,但就公司发展而言,如果没有在行业内的长久历练,凭什么提出更有价值的建议呢?有一些评论文章,总是拿空泛的理想说事儿,我承认这些重要,但是脱离现实的理想,是不是有点太书卷气了。
对评论者而言,写的多了大概有一种挥斥方遒的感觉,《网络江湖36计》(这是本关于中国互联网历史的好书,虽然书名给人印象不好)中,对这样的IT媒体人已经有了深入的分析:写的多了,和IT大佬们坐而论道多了,渐渐以为自己也很有本事,跃跃欲试,殊不知真正做事时,想到并不意味着做到,你虽然看得高,却没有把脚踩在地下,很可能会摔下来。
指方向、谈战略、论趋势也许容易,真正做起来,千头万绪,方知不易啊。
上学期有一堂课,我们小组的展示内容是互联网相关的话题,作为小组代表的我回答了几个问题,当时有点侃侃而谈,下来感觉自己话说的太大,不实在,心里发虚,仔细想想为什么心虚呢?就是因为,什么样的高度就该说什么样的话,积累没到,硬要拔高,自然不合适。
现在这个阶段,大而空泛的东西少看一些,多看看贴近实际的,"在事上磨练",才是正经。
Published:
01 Apr 2011
移动搜索文献调研结果分为4部分:
1.Review(综述类)
2.Mobile search features(移动搜索特点研究)
3.Hot topics(热点研究方向)
4.Research Resources(研究资源:有关会议、组织等)
Review
- [1] F. Tsai, M. Etoh, X. Xie, and W. Lee, "Introduction to mobile information retrieval," IEEE Intelligent Systems, 2010, pp. 11-15.
- K. Church, B. Smyth, and P. Cotter, "Mobile information access: A study of emerging search behavior on the mobile Internet," ACM Transactions on the, vol. 1, May. 2007, p. 4-es.
- Roto, V. (2006), Search on mobile phones. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 57: 834–837. doi: 10.1002/asi.203
- S.G. Nikolov, R. Compañó, M. Bacigalupo, and C. Feijóo, "What is Missing for the Full Deployment of Mobile Search Services ? Results from a Survey with Experts," Technology, 2010, pp. 1-9.
- "Introduction to Mobile Search,"Technical report,Mobile Marketing Association。January 2006 http://www.mmaglobal.com/mobilesearchintro.pdf
- Mobile Search Tutorial
- M. Jones, Mobile Search Tutorial, 2009.http://www.comp.lancs.ac.uk/~rukzio/mobilehci2009tutorials/Jones_MobileSearch.pdf
Mobile search features
- T. Sohn, K. a Li, W.G. Griswold, and J.D. Hollan, "A diary study of mobile information needs," Proceeding of the twenty-sixth annual CHI conference on Human factors in computing systems - CHI '08, 2008, p. 433.
- Kamvar, M., Baluja, S. A Large Scale Study of Wireless Search Behavior: Google Mobile Search. In Proc. of CHI 2006, pp. 701-709.
- J. Yi, F. Maghoul, and J. Pedersen, "Deciphering Mobile Search Patterns : A Study of Yahoo ! Mobile Search Queries," Distribution, 2010, pp. 257-266.
- K. Church, B. Smyth, K. Bradley, and P. Cotter, "A large scale study of European mobile search behaviour," Proceedings of the 10th international conference on Human computer interaction with mobile devices and services - MobileHCI '08, 2008, p. 13.
- Lee, I. et al. Use Contexts for the Mobile Internet: A Lon- gitudinal Study Monitoring Actual Use of Mobile Internet Services. Journal of Human-Computer Interaction, 18(3), pp. 269-292.
- M. Kamvar, M. Kellar, R. Patel, and Y. Xu, "Computers and iphones and mobile phones, oh my!," Proceedings of the 18th international conference on World wide web - WWW '09, 2009, p. 801.
Hot topics:
Two main themes characterize research in this growing area: context awareness and content adaptation[1].
注:本部分的分类和部分参考文献来自文献[1]中的总结。
context awareness:
Mobile devices have more features than their computer counterparts, including location information, built- in cameras, and certain social networks.
- F.S. Tsai et al., "Design and Development of a Mobile Peer-to-Peer Social Networking Application," Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 36, no. 8, 2009, pp. 11077–11087.
- S. Mizzaro and E. Nazzi, "Retrieval of context-aware applications on mobile devices: how to evaluate?," Proceedings of the second, 2008, pp. 65-71.
Multimedia:
- Mobile search can also be enhanced with images, audio, video, and their combinations for a richer experience.
- X. Xie et al., "Mobile Search with Multimodal Queries," Proc. IEEE, vol. 96, no. 4, 2008, pp. 589–601.
- X. Fan, X. Xie, Z. Li, M. Li, and W.-ying Ma, "Photo-to-Search : Using Multimodal Queries to Search the Web from Mobile Devices," Science And Technology, 2005, pp. 143-150.
Location-based search
- T. Tezuka, T. Kurashima, and K. Tanaka, "Toward Tighter Integra- tion of Web Search with a Geographic Information System," Proc. 15th Int'l Conf. World Wide Web (WWW 06),
- D. Choi, "Personalized local internet in the location-based mobile web search," Decision Support Systems, vol. 43, Feb. 2007, pp. 31-45.
- M. Jones, G. Buchanan, R. Harper, P.-louis Xech, J.J.T. Ave, and C. Uk, "Questions Not Answers : A Novel Mobile Search Technique," Science, 2007, pp. 155-158.
Extraction of useful semantics
- K.Y. Yee et al., "OntoMobiLe: A Generic Ontology-Centric Service-Oriented Architecture for Mobile Learning," Proc. 10th Int'l Conf. Mobile Data Management: Systems, Services and Middleware (MDM 09), IEEE CS Press, 2009, pp. 631–636.
- Data mining of query logs, clicks, and Web traffic on mobile devices
- A.T. Kwee and F.S. Tsai, "Mobile Novelty Mining," Int'l J. Advanced Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing, to be published, 2010.
Content Adaptation
-
Small screens and low-power and low-memory devices.
- Many of these areas can adapt existing IR technologies for mobile data, such as content-based extraction, indexing, annotation, and retrieval of mobile data
-
power and efficiency distinguish the really useful algorithms
Content adaptation for smalldisplay devices includes automatic summarization and personalization in mobile information
-
K. Church and B. Smyth, "Who , What , Where & When : A New Approach to Mobile Search," 2008, pp. 309-312.interface technologies(interaction)
-
A. Karlson, G. Robertson, and D. Robbins, "FaThumb: a facet-based interface for mobile search," Proceedings of the, 2006, pp. 711-720.
-
Kamvar, M. and Baluja, S. 2008. Query suggestions for mobile search: understanding usage patterns. In Proceeding of the Twenty-Sixth Annual SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (Florence, Italy, April 05 - 10, 2008). CHI '08. ACM, New York, NY, 1013-1016. DOI= http://doi.acm.org/10.1145/1357054.1357210
Research Resources[1]
Related Conferences
- • International Conference on Ubiquitous Computing (UbiComp), www.ubicomp.org
- • 11th International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction with Mobile Devices and Services (MobilHCI 09), www.mobilehci09.org
- • Eighth International Conference on Pervasive Computing (Pervasive 10), http://pervasive2010.cs.helsinki.fi
- • 11th International Conference on Mobile Data Manage- ment (MDM 10), http://sce.umkc.edu/mdm2010
- • International Workshop on Mobile Information Retrieval for Future (MIRF), http://ir.kaist.ac.kr/mirf
- • International Workshop on Mobile Media Retrieval (MMR 09), http://www3.ntu.edu.sg/home/wukui/mmr
- • International Workshop on Mobile Information Retrieval (MobIR 08), http://www3.ntu.edu.sg/home/efstsai/ MobIR
Related Organizations
- • ACM SIGIR, information retrieval; www.sigir.org
- • ACM SIGMOBILE, mobility of systems, users, data, and computing; www.sigmobile.org
- • ACM SIGSPATIAL, applications involving spatial information, www.sigspatial.org
Published:
18 Mar 2011
这两天在考虑研究方向的选择问题,发现自己对计算机专业的学科和知识体系并不了解,就做了一些调研,找到了一些有用的资料。
最权威的资料是ACM和IEEE一起发布的计算机领域的课程体系——computing curricula,官方网站是http://www.acm.org/education/curricula-recommendations,在这里可以下载到两大协会保持更新的计算领域各学科课程体系。我在这里第一次知道,计算下面有5个子学科——Computer Science, Computer Engineering, Information Systems, Information Technology和Software Engineering。ACM为每个方向都给出了详实的学科综述报告,每份报告都有该方向的情况概要和具体课程(知识)体系。读完这几份报告你会对计算机领域有一个宏观上的认识,对自己的研究方向在这个大学科所处的位置也就有了概念。
上面的知识体系有个简单的翻译,在长春工业大学的网站上,可以参考:
http://jsj.ccut.edu.cn/sjjg/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=633&Itemid=222。
除了权威报告,一些计算机领域人士总结的知识体系也可以借鉴:
计算机 知识体系结构的构建:
http://xiantao.blog.hexun.com/5803769_d.html
理想的计算机科学知识体系:
http://www.penglixun.com/study/computer_science_knowledge_hierarchy.html>
除了选择研究方向,如果想补充技术知识,这些大牛们总结的体系也是不错的参考资料。
ps:也许你像我一样,看到这些体系后发现自己其实很无知,那就赶紧开始学习吧。
Published:
18 Mar 2011
实验室有个项目,需要做一个手机网站的站内搜索引擎,我和几个同学开始一起搭建demo。经过前期的资料调研,发现一个奇怪的现象:有关移动搜索的技术资料几乎没有(有一本中文的书没有很大价值),有关手机建站的技术资料,基本都是2000年左右出版的(你还记得那时的手机长什么样吗?)。
资料少估计不是搜索的方式问题,我试了中英文搜索、换了一些关键词,收获甚微。如果说手机wap网站的技术没有多少进步所以产生这种情况,看看web方面,有很多质量参差不齐的技术书在丰富着市场。现在下结论还太早,观察一段时间再说。
没有现成资料只好自己分析了,结合搜索技术,wap方面的资料和已经有的移动搜索产品,我们觉得,如果不考虑手机的特点带来的交互方式变化,那么移动搜索只是在抓取页面和页面展示上有所不同,后台的搜索服务目前可以认为原理不变。
基于此,我们的第一个"产品"demo,就是根据lucene里的demo,把jsp代码改为了输出wml页面的方式,这样部署在web服务器上,手机就可以访问了。
第一步的工作只是个实验,后面要做的才是真正的工作。接下来就要陪伴这个小产品慢慢成形。
Published:
18 Mar 2011